β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) is a physiologically circulating nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) precursor that increases cellular levels of NAD+ and improves various age-related diseases.
There is an inextricable link between aging and tumorigenesis, especially involving aberrant energy metabolism and cell fate regulation in cancer cells.
In recent years, it has been confirmed that NMN plays an active role in immunotherapy (PD-L1 related), CAR-T therapy, NK cell therapy and other cancer therapies through mechanisms such as delaying immune cell aging and enhancing immune cell function.
It has a palliative effect and is expected to become an adjuvant intervention during chemotherapy.
Recently, a research team studied the role of high-dose NMN in lung adenocarcinoma.
The study found that high-dose β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide promotes ferroptosis through NAM-mediated SIRT1-AMPK-ACC signaling, emphasizing the tumor impact of high-dose NMN in manipulating cancer cell metabolism and providing a new perspective for clinical treatment of lung adenocarcinoma patients.
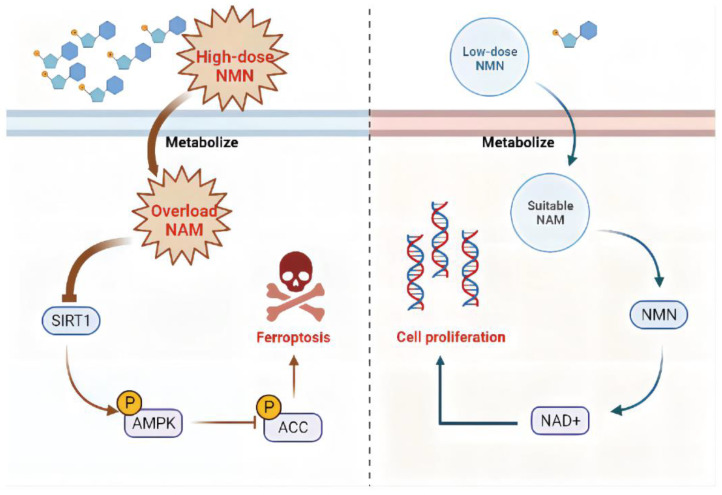
The findings showed that local treatment with high-dose NMN strongly inhibited tumor growth and induced tumor ferroptosis in lung adenocarcinoma cells.
- High-dose NMN (100 mM) inhibited lung adenocarcinoma A549 and SPCA1 cell proliferation and promoted cell death, while low-dose (10 mM) treatment produced the opposite effect;
- Cell death induced by high-dose β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide occurs through ferroptosis;
- High-dose β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide treatment mainly induces intracellular NAM overload and triggers ferroptosis;
- High-dose β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide induces tumor ferroptosis by overloading the NAM-mediated SIRT1-AMPK-ACC pathway.
The study also further showed that the combination of NAMPT inhibitor FK866, a potential tumor therapeutic agent, with high-dose NMN local treatment increased the efficacy of tumor suppression in vitro and in vivo.
The research team believes that it is necessary to further explore strategies to optimize the NMN response in lung adenocarcinoma patients, and proposed a model of the effect of β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide on the regulation of ferroptosis in lung adenocarcinoma cells.
In an earlier study, some researchers believed that β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide might accelerate the further deterioration of cancerous tissues, which attracted a lot of attention.
The study found that this study of NMN on lung adenocarcinoma also showed that high doses of β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide can limit tumor growth.

Whether β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide also requires the same high dose in other cancers remains to be studied. What can be confirmed is that more and more studies have proved that NMN not only does not cause cancer, but also helps to fight tumors.
In addition, although NMN anti-tumor research has made continuous progress, and clinical studies on healthy people have shown safety, it is not recommended for cancer patients at this stage.
We provide high-quality β-nicotinamide mononucleotide raw materials, and the products are exported to Europe, America, South Korea, India and other parts of the world. If you are interested in our products, please feel free to contact us, we will be happy to provide any information you need.












Hello. And Bye.